close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-05 Origin: Site









Aluminum foil laminated PET PE film acts as a high-performance shield in packaging, combining multiple layers to create strong barriers against light, oxygen, and moisture. This multilayer structure protects products by blocking contamination and preserving freshness, as seen in industry cases with dairy products from leading brands. Scientific studies confirm that aluminum foil laminated PET PE film delivers extended shelf life and superior protection for foods like dried barberries and ready meals. Strong barrier performance, flexibility, and durability make this film a reliable choice for maintaining product quality.
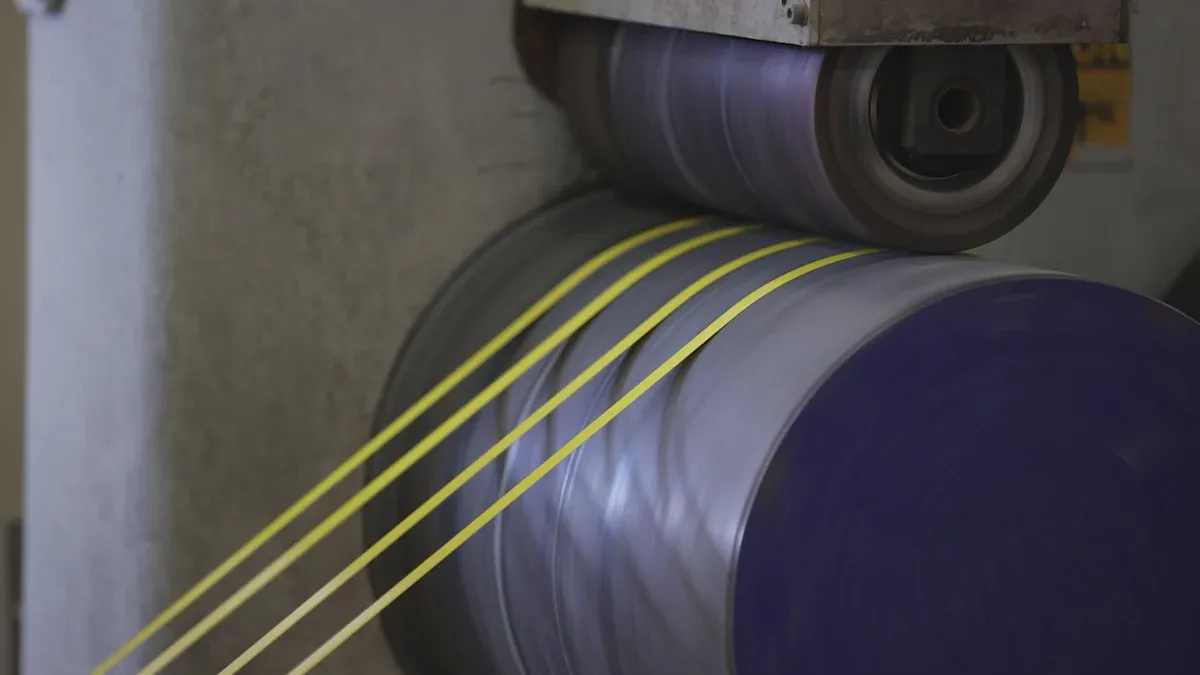

Aluminum foil laminated PET PE film is a specialized packaging material made by bonding three distinct layers: polyester (PET), aluminum foil, and polyethylene (PE). Manufacturers use a dry lamination process, which involves coating the aluminum foil with adhesive after surface treatment. They then press the PET and PE films onto the foil using heat and pressure. The aluminum foil layer usually ranges from 6 to 20 microns in thickness. PET and PE layers are selected based on the needs of the product, such as barrier strength, flexibility, and environmental resistance.
Each layer brings unique properties to the film. PET provides high tensile strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to UV light. The aluminum foil acts as a nearly perfect barrier to oxygen, moisture, and light. PE offers flexibility, impact resistance, and excellent heat sealability. Together, these layers create a packaging film that is strong, flexible, and highly protective.
Note: The combination of these materials results in a film that is lightweight, customizable, and suitable for a wide range of packaging applications.
| Component | Key Properties |
|---|---|
| PET | High strength, UV resistance, low moisture absorption, printable surface |
| Aluminum | Excellent barrier to gases, moisture, light, and odor; high thermal conductivity; puncture resistance |
| PE | Flexible, impact resistant, water vapor barrier, chemical resistance, heat sealable |
Aluminum foil laminated PET PE film plays a vital role in modern packaging. This film protects products from environmental threats such as moisture, oxygen, and light. The PET layer provides strength and serves as a printable surface for branding and product information. The aluminum foil layer blocks nearly all gases and light, preventing spoilage and flavor loss. The PE layer allows for secure heat sealing, which keeps the package airtight and tamper-resistant.
Laminated aluminum foil is widely used in food, pharmaceutical, and industrial packaging. It helps maintain product freshness and quality by preventing contamination and extending shelf life. For example, snack foods, dairy products, and ready meals often use this film to keep contents safe and appealing. The film’s flexibility allows it to conform to different shapes, reducing empty space and protecting delicate items.
Aluminized PET film, a related material, also finds use in packaging. It offers similar barrier properties but uses a much thinner layer of aluminum, making it lighter and more cost-effective for some applications. Both laminated aluminum foil and aluminized PET film provide strong protection, but the full laminate structure offers superior mechanical strength and durability.
Manufacturers choose aluminum foil laminated PET PE film when they need packaging materials that combine barrier performance, mechanical strength, and flexibility. The film’s ability to block moisture, oxygen, and light makes it ideal for products that require extended shelf life and consistent quality. Laminated aluminum foil also supports high-speed packaging lines and can be tailored to meet specific product needs.
️ Tip: Laminated aluminum foil and aluminized PET film both offer excellent protection, but the full laminate structure is preferred for demanding applications where maximum barrier and strength are required.
Laminated aluminum foil uses a multi-layer structure to deliver strong protection and performance in packaging. Each layer serves a unique function, and together, they create a film that meets the demands of modern packaging.
The aluminum foil layer sits at the core of the structure. This layer acts as a powerful barrier against moisture, oxygen, and light. Manufacturers often use aluminum foil with a thickness between 8 and 20 microns for food and pharmaceutical packaging. The foil provides high reflectivity, thermal insulation, and flame retardancy. However, it remains fragile and cannot seal on its own. For this reason, the foil needs protection from both sides by other films.
The PET layer forms the outer surface of the laminated aluminum foil. PET, or polyethylene terephthalate, offers high mechanical strength and flexibility. It also resists heat and chemicals, making it ideal for packaging. PET serves as the print substrate, allowing brands to add graphics and product information. This layer protects the aluminum foil from damage and supports the overall structure.
The PE layer, usually made from low-density polyethylene (LDPE), forms the inner surface of the film. This layer provides heat sealability, which is essential for creating airtight and tamper-resistant packages. PE also adds flexibility and impact resistance. It ensures the package remains intact during handling and storage.
Note: The combination of these three layers—PET, aluminum foil, and PE—creates a film that balances barrier performance, strength, and sealability.
| Layer | Main Functions |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Foil | Barrier to moisture, oxygen, and light; thermal insulation; structural stability |
| PET | Print substrate; mechanical strength; flexibility; protection for aluminum foil |
| PE (LDPE) | Heat sealability; forms inner surface; impact resistance |
The layers in laminated aluminum foil work together to enhance the film’s performance. PET provides a tough, printable outer surface and shields the aluminum foil from physical damage. The aluminum foil delivers the highest barrier properties, blocking almost all gases and light. PE forms the inner sealing layer, allowing the package to be heat-sealed and ensuring product safety.
Manufacturers use advanced lamination methods to bond these layers. Extrusion lamination, where a melt-extruded polymer bonds the layers, gives strong adhesion and durability. Solvent lamination, which uses adhesives, is chosen for special cases like adding extra oxygen barriers. Surface treatments such as corona or passivation improve adhesion and reduce defects.
The interaction of these layers prevents weaknesses like foil tearing or pinholes. The PET layer reinforces the structure, while the PE layer ensures a secure seal. This synergy results in a film that offers high barrier protection, mechanical strength, and flexibility. Laminated aluminum foil outperforms single-layer films and even aluminized pet film in demanding applications.
️ Tip: Aluminum foil laminated with plastics, such as PET and PE, creates aluminum plastic laminates that combine the best features of each material. This structure supports a wide range of packaging needs, from food to pharmaceuticals.
| Layer | Role and Properties | Contribution to Film Performance |
|---|---|---|
| PET (outer) | High strength, heat resistance, chemical stability, printable surface | Mechanical strength, printability, moderate moisture barrier |
| Aluminum Foil | Barrier to gases, moisture, and light; near-zero water vapor and oxygen transmission | Highest barrier, thermal insulation, but needs protection and sealing support |
| PE (inner) | Sealant due to melting point, flexibility | Heat sealability, package protection, scalability |
Aluminized pet film uses a much thinner aluminum layer, which makes it lighter but less protective than laminated aluminum foil. For products that need maximum shelf life and safety, laminated aluminum foil remains the preferred choice.
Aluminum foil laminated PET PE film delivers outstanding barrier performance, making it a top choice for flexible packaging. The multilayer structure blocks moisture, oxygen, and light, which are the main causes of product spoilage. Laboratory tests show that a foil thickness of 1 mil or greater is almost pinhole free, resulting in minimal permeation. The PET layer protects the aluminum foil from chemical degradation and improves sealing. The combination of these layers creates a robust barrier system that keeps products fresh and safe.
The oxygen transmission rate (OTR) and water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) for these films are extremely low. For example, a coated PE-based film measured an OTR of 0.18 ± 0.01 × 10⁻⁶ mol/m²/s and a WVTR of 2.84 ± 0.22 × 10⁻⁵ g/m²/s. These values indicate a very high barrier to oxygen and moisture. The film also provides strong UV-C light shielding, which protects sensitive products from light exposure.
Compared to single-layer films, the PET/AL/PE laminated film offers superior barrier protection. The aluminum foil layer achieves near-zero OTR and WVTR values, while the PET and PE layers add strength and sealability. Single-layer films, such as metallized PET, cannot match this level of moisture and oxygen resistance. The laminated structure also improves printability and makes the film more practical for packaging sensitive products.
Aluminum foil stands out as the best barrier material among flexible packaging substrates. Although tiny pinholes may exist, the overall barrier performance remains unmatched. The addition of oxygen scavengers or moisture barrier materials, such as cyclic olefin copolymers, can further enhance the film’s protective properties in specialized applications.
️ Note: The high barrier properties of aluminum foil laminated PET PE film help extend shelf life and maintain product quality, especially for foods, pharmaceuticals, and other sensitive items.
Mechanical strength is another key property of aluminum foil laminated PET PE film. The multilayer design increases both tensile strength and puncture resistance, making the film suitable for packaging fragile or heavy products. Pure aluminum foil has a tensile strength of about 70 MPa, while work-hardened or alloyed foils reach 120–150 MPa. Laminated films with a 12–20 µm foil gauge and PET or OPP layers typically achieve puncture resistance above 10 N.
| Property | Measured Values / Description |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Pure aluminum foil: ~70 MPa; Work-hardened/alloyed foils: 120–150 MPa |
| Puncture Resistance | >10 N for laminated films with 12–20 µm foil gauge and PET/OPP layers |
| Application Notes | Enhanced strength and puncture resistance, ideal for fragile products |
Tests at Clemson University confirmed that puncture resistance increases over curing time and stabilizes after several hours. The mode of failure shifts from delamination to single substrate failure as the film cures, showing improved durability. PET/NYLON/PE films, which are similar in structure, offer even higher tensile strength and scuff resistance. These films withstand the stresses of packaging heavy or sharp-edged products, thanks to their chemical stability and resistance to abrasion.
Aluminized BOPET films also demonstrate high tensile strength and elongation at break, contributing to their durability. The combination of heat and puncture resistance, along with moisture-blocking capabilities, makes these films a reliable choice for protecting products from physical damage during transport and storage.
Flexibility is essential for modern flexible packaging, and aluminum foil laminated PET PE film excels in this area. The PET layer adds strength and stability, while the PE layer provides sealability and impact resistance. The aluminum foil, although not flexible on its own, gains flexibility when combined with PET and PE. This combination allows the film to bend, fold, and conform to various packaging shapes without losing its barrier performance.
Flexibility tests, including tensile and 180° peel tests, reveal that the film’s mechanical behavior depends on thickness, direction, and test method. The elastic modulus and yield stress vary between the machine direction (MD) and transverse direction (TD). Peel forces in the TD are higher, showing strong plastic deformation due to chain re-orientation. Method B, which uses adhesive tape, prevents full-field plastic deformation and provides more accurate peel strength results.
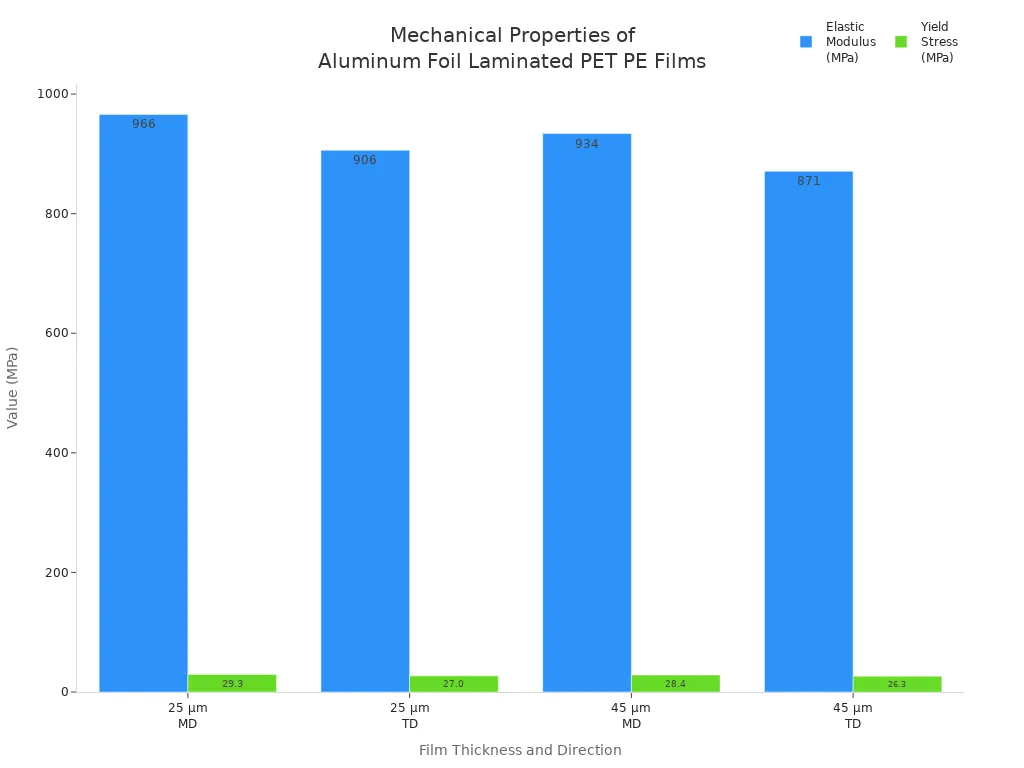
| Thickness (µm) | Direction | Elastic Modulus (MPa) | Yield Stress (MPa) | Peel Force Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | MD | ~966 | ~29.3 | Lower peel force, limited elongation, strain hardening |
| 25 | TD | ~906 | ~27.0 | Higher peel force, strong plastic deformation |
| 45 | MD | ~934 | ~28.4 | Slightly lower modulus, similar to 25 µm MD |
| 45 | TD | ~871 | ~26.3 | Higher peel force, more plastic deformation |
The flexibility of aluminum foil laminated PET PE film supports a wide range of packaging formats, such as bags, pouches, and roll stock. The film can be customized with extra layers or coatings to enhance strength or heat resistance. Flexible pouches made from this film protect sensitive products like pet foods by providing high barrier protection against light, oxygen, and moisture. The film’s adaptability and enhanced durability make it suitable for diverse packaging needs, ensuring seal integrity and product safety.
Tip: The flexibility and high barrier properties of aluminum foil laminated PET PE film allow manufacturers to create packaging that is both protective and easy to use, meeting the demands of modern consumers.
Aluminum foil laminated PET PE film stands out for its strong thermal insulation abilities. The film’s design uses several layers, each with a special job. The aluminum foil layer reflects heat, light, and UV rays. This reflective property helps keep heat from passing through the packaging. In fact, the film can reflect up to 97% of radiant heat. This means less heat enters or leaves the package, which helps keep the inside temperature steady.
The multilayer structure also includes an outer resistance layer and a heat-sealing layer. These layers add extra protection against heat and help the film resist high temperatures. The adhesive layers between them improve bonding strength and make the film more resistant to heat. The film stays soft and flexible because of special thermal treatments during manufacturing. It does not become stiff or rusty like regular aluminum foil. It also does not build up static electricity, which adds to its insulation performance.
The film’s ability to block moisture is another key part of its insulation. The aluminum foil layer acts as a moisture barrier, keeping the inside dry. This is very important for products that need to stay at a certain temperature and humidity level. The film’s structure also protects against environmental factors like UV rays, which can damage sensitive products.
These thermal insulation properties offer several benefits for packaging, especially for temperature-sensitive goods:
The film reflects most radiant heat, which helps keep food and medicine at safe temperatures.
The moisture barrier keeps the inside dry, protecting products from spoilage.
The strong structure gives the film durability and helps it last longer, even in tough conditions.
The film’s design protects against UV rays and other environmental threats.
Manufacturers use aluminum foil laminated PET PE film to package foods, pharmaceuticals, and other products that need stable temperatures. The film’s insulation helps extend shelf life and maintain product quality. It also keeps products safe during shipping and storage.
Tip: When packaging temperature-sensitive items, choosing a film with strong thermal insulation and moisture protection can make a big difference in product safety and shelf life.
Manufacturers use several methods to create aluminum foil lamination for packaging. Each method helps combine different layers, such as PET, aluminum foil, and PE, into a single, high-performance film. The most common technique is extrusion lamination. In this process, a machine coats molten resin onto a moving substrate. Workers then press the layers together while the resin is still hot. This method works well for multilayer films, especially in medical and food packaging.
Surface treatments play a key role in aluminum foil lamination. Operators often use corona discharge, plasma, or chemical primers to improve adhesion between layers. These treatments help bond polyester to polyethylene or aluminum foil to PE, making the structure strong and reliable.
Other lamination methods include:
Dry Bond Lamination: Technicians apply adhesives to the surface and dry them before joining the layers. This method suits non-porous materials.
Wet Bond Lamination: Workers apply adhesive and dry it during the lamination process. This method works best when one layer is porous.
Hot-Roll Lamination: Machines use heat and pressure in a roll-to-roll process. This method is ideal for thermoplastic polymers like PE and allows for fast production.
Manufacturers can use step-by-step or one-step processes. The step-by-step method laminates two layers at a time, with partial curing between steps to reduce defects. The one-step method combines three or four layers at once, but it requires special equipment.
Note: The choice of lamination method depends on the product’s needs, the type of aluminum foil for lamination, and the desired barrier properties.
Quality control ensures that aluminum foil lamination meets strict standards for safety and performance. Operators check each stage of production to prevent defects and maintain consistency.
Key quality control measures include:
Visual Inspection: Workers look for surface defects, such as scratches, dents, or air bubbles. They also check color and printing quality.
Dimensional and Thickness Verification: Technicians measure each layer and the total thickness using precise tools. This step ensures the film fits packaging machines.
Mechanical Property Testing: Teams test tensile strength, elongation, puncture resistance, and bond strength. These tests confirm the film’s durability.
Barrier Property Tests: Specialists measure water vapor transmission rate (WVTR), oxygen transmission rate (OTR), and light transmission. These tests show how well the film protects products.
Chemical Property Tests: Analysts check for extractables, leachables, and chemical resistance to ensure product safety.
Pinhole Detection: Workers use light, electrical, or gas methods to find tiny holes that could weaken the barrier.
Microbial Cleanliness: Teams test for microbial and particulate contamination, especially for pharmaceutical packaging.
Manufacturers also select high-quality aluminum alloys and standardize alloy types to improve quality control. They verify raw material properties, such as thickness and hardness, through supplier certificates and in-house testing. Advanced rolling mills help produce consistent foil gauges and widths. Operators maintain a clean environment, control temperature and humidity, and use accurate slitting and winding techniques to prevent defects.
✅ Tip: Continuous process optimization and regular equipment maintenance help ensure that aluminum foil lamination meets customer and regulatory requirements.

Food packaging relies heavily on laminated aluminum foil for its outstanding ability to protect products. This material keeps food fresh by blocking moisture, oxygen, and light. Many common foods use this technology, including:
Tea
Coffee
Fried food
Snacks
Cookies
Biscuits
Chocolate
Nuts
Oats
Protein powder
Milk powder
Pet treats
Laminated aluminum foil provides a strong barrier that preserves fats, oils, and vitamins. It prevents oxidation and keeps products like baby food, freeze-dried foods, teas, and spices safe from moisture loss and UV damage. The PET/AL/PE structure maintains aroma, flavor, and texture. Coffee packaging often uses PET/ALU/LDPE or PET/ALU/PET/LDPE laminates, which offer robust protection for roasted beans. Flexible laminated aluminum foil packaging has replaced metal cans for many foods, offering similar or better shelf life at a lower cost. The structure also reduces risks of metal migration and corrosion, making it safer than some alternatives.
Pharmaceutical packaging demands high standards for safety and product integrity. Laminated aluminum foil meets these needs by providing a strong barrier against moisture, oxygen, and light. PET/AL/PE films deliver enhanced strength and chemical stability. These films help maintain the quality of sensitive medicines and medical devices. The multi-layer structure can be modified with coatings to improve barrier performance further. This makes it ideal for products that require extended shelf life and protection from contamination.
Aluminum foil laminated films offer excellent microbial barriers and withstand sterilization processes. The healthcare industry uses them for single-use medical devices, diagnostics, and pharmaceuticals. The structure resists punctures and tears, ensuring that medicines remain safe. These films comply with major safety standards, such as FDA and EU regulations, and prevent chemical migration. Over 80% of blister packs worldwide use laminated aluminum foil as the primary barrier, showing its effectiveness in pharmaceutical packaging.
Tip: Laminated aluminum foil not only protects against environmental threats but also supports tamper evidence and dosage accuracy in pharmaceutical packaging.
Aluminum foil laminated bags play a vital role in both industrial and consumer packaging. These bags block light, oxygen, and moisture, which helps maintain product quality and freshness. They protect against oxidation, moisture absorption, and spoilage. Food packaging uses these bags for baked goods, nuts, dried fruits, and ready-to-eat meals. The beverage industry relies on them for coffee, tea, and energy drinks to preserve aroma and flavor.
Pharmaceutical packaging also benefits from aluminum foil laminated bags. They keep tablets, capsules, and powders safe from moisture and light. These bags come in various styles, such as flat bags, pillow bags, and four-side seal bags. Features like resealable zippers, tear notches, and clear windows add convenience. The bags are durable, puncture-resistant, and suitable for thermal processing. Stand-up pouches and vacuum bags offer airtight closures, while custom printing supports branding.
Aluminum foil laminated bags provide excellent barrier protection for food and sensitive products.
They are lightweight, flexible, and suitable for many shapes and sizes.
Heat sealing ensures airtight packaging.
High barrier bags are used for pharmaceuticals and sensitive items.
Customization options meet diverse packaging requirements.
The aluminum foil laminated bag with PET combines natural looks with strong barrier properties, making it suitable for coffee and other specialty foods. This versatility in applications highlights why laminated aluminum foil remains a top choice for modern packaging.
Many industries rely on aluminum foil laminated PET PE film for packaging products that need strong protection. This material does more than keep food fresh. It also plays a key role in keeping chemicals, electronics, and sensitive materials safe during storage and transport.
Factories often use aluminum foil laminated bags to package chemicals. These bags have three layers. The outer PET layer gives strength and resists heat. The middle aluminum foil layer blocks gases, moisture, and light. The inner PE layer allows for heat sealing. This structure keeps chemicals stable by stopping air and water from getting inside. It also protects against UV light, which can damage some products. Companies that make powders, adhesives, and specialty chemicals choose these bags to prevent leaks and keep their products pure.
Electronics manufacturers also use aluminum foil laminated bags. These bags shield sensitive parts from static electricity, moisture, and dust. For example, computer chips and circuit boards need protection from even small amounts of water or oxygen. The strong barrier of the aluminum foil layer helps prevent corrosion and failure. Some bags include extra layers, such as nylon, to add strength for heavy or sharp items.
Industrial packaging sometimes uses PET films coated with aluminum oxide (AlOx). This coating creates a thin, clear layer that blocks oxygen, moisture, and light. The AlOx-coated PET film is important for packaging sensitive products like chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. It keeps products safe from contamination and helps them last longer. The film is also food-safe, so it can be used in food packaging and other demanding applications.
Aluminum foil laminated PET PE film works well for packaging liquids and powders. The film’s sealability and mechanical strength prevent spills and damage. Factories use these films for lubricants, inks, and cleaning agents. The film’s barrier properties help maintain product quality and extend shelf life.
Note: Industrial users value aluminum foil laminated bags for their ability to protect against leaks, oxidation, and environmental threats. These bags help companies meet safety standards and reduce waste.
The wide range of industrial uses shows the versatility of aluminum foil laminated PET PE film. Its strong barrier, heat resistance, and sealability make it a top choice for packaging in many industries.
Aluminum foil laminated PET PE film presents challenges for recycling. The combination of metal and plastic layers makes separation difficult. Most recycling centers cannot process these multilayer films because the aluminum foil and polymer layers bond tightly. This structure limits the recovery of both the metal and the plastic. Inks, adhesives, and additives further complicate recycling efforts. As a result, the recyclability rate for aluminum foil laminated PET PE film remains lower than that of other multilayer packaging materials.
Unlike single-layer films such as PE or PET, which many companies recycle, multilayer films with aluminum foil often end up in landfills or incinerators. The presence of aluminum in the film can cause the recycled plastic to turn gray, reducing its value and usability. Industry guidelines recommend avoiding the use of polyolefins combined with aluminum foil in packaging because this mix lowers the quality of recycled materials. Waste management systems also struggle to sort and process these complex films, making large-scale recycling rare.
♻️ Note: Improving recyclability requires new designs and materials that maintain barrier performance while allowing for easier separation and recovery.
Packaging companies and material scientists have introduced several innovations to address the environmental impact of aluminum foil laminated PET PE film. Many now focus on replacing traditional aluminum foil with recyclable mono-material laminates. For example, new polypropylene (PP) based laminates use oriented polypropylene (OPP) films to provide strong barriers against moisture, oxygen, and light. These films, such as the Metallyte™ and Bicor™ series, match the protective qualities of aluminum foil but allow for mechanical recycling.
Recent advances include the use of high-barrier coatings like AlOx (alumina) or SiOx (silica oxide) applied to polyolefin films. These coatings create a thin, transparent barrier that blocks gases and moisture. By using the same material for both the barrier and sealing layers, manufacturers simplify the structure and improve recyclability. Some companies, like ExxonMobil, have developed MDO-PE/PE laminates that offer excellent barrier properties and fit into existing recycling streams.
Innovations also extend to production methods. Solvent-free adhesives and five-layer blown film processes reduce environmental impact. Companies like Momar Industries produce high-barrier metallized PET films that are recyclable and made in FDA-compliant facilities. These efforts support food safety and environmental goals.
Sustainability improvements have led to measurable reductions in environmental footprint. For example, replacing aluminum foil with metallized polymer laminates can cut metal depletion by up to 71%, fossil depletion by 21%, and global warming potential by half. Embodied energy use drops by about 25%. The chart below shows these reductions:
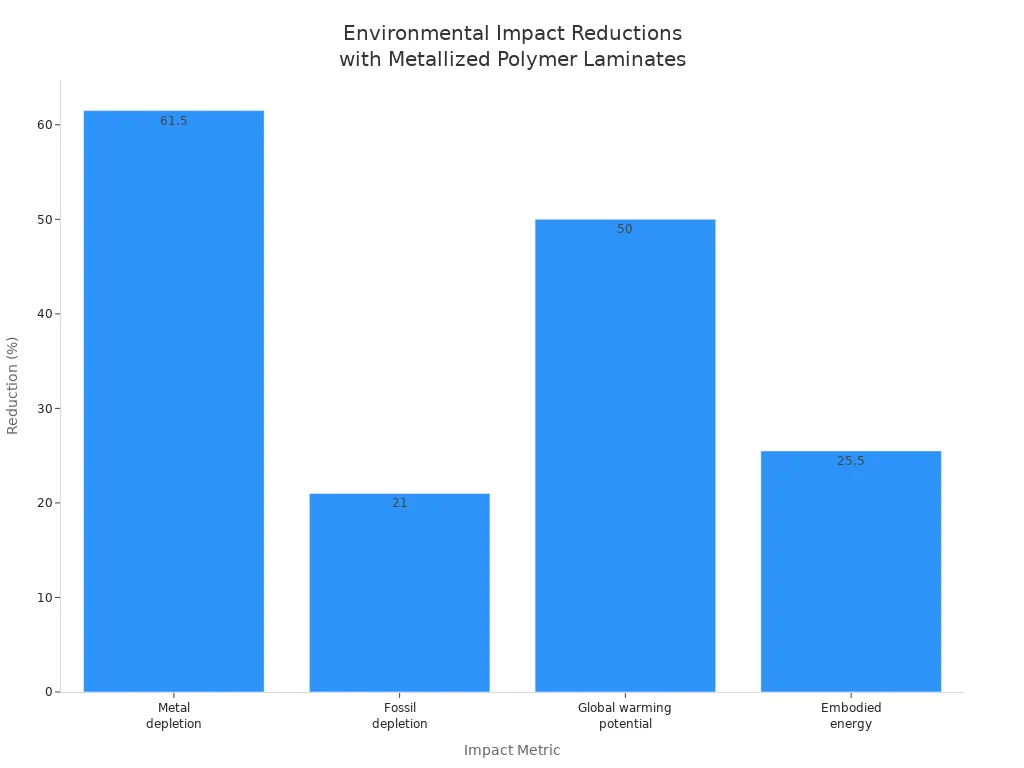
Tip: Choosing packaging made from recyclable mono-material laminates or films with advanced barrier coatings helps reduce waste, conserve resources, and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
When companies select packaging materials, they often compare laminated aluminum foil with other options like aluminized PET film. Each material offers unique strengths and weaknesses. The table below highlights key differences:
| Factor | Laminated Aluminum Foil | Aluminized PET Film |
|---|---|---|
| Barrier Performance | Superior barrier: near-zero moisture & oxygen permeability; complete light blockage | Moderate barrier: very good moisture and oxygen resistance but not absolute |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, prone to cracking under stress | Highly flexible and durable |
| Cost | Higher raw material and production costs | Lower cost due to lightweight and simpler production |
| Environmental Impact | Fully recyclable but energy-intensive production | Recyclability depends on local facilities; newer biodegradable metallized films emerging |
| Typical Applications | Premium, long-shelf-life, sensitive products (e.g., retort pouches, ready-to-eat meals) | High-volume flexible packaging, electronics shielding, snack bags |
Laminated aluminum foil stands out for its barrier performance. It blocks almost all moisture, oxygen, and light, which helps keep food and medicine safe for longer periods. This makes it the preferred choice for products that need maximum protection. Aluminized PET film, on the other hand, is more lightweight and cost-effective. It works well for snack bags and electronics but does not provide the same level of protection. Laminated aluminum foil also offers better recyclability, although its production uses more energy. Companies often choose it for premium or sensitive products where shelf life and safety matter most.
Tip: For products that require the highest level of protection, laminated aluminum foil remains the top choice despite higher costs and lower flexibility.
The packaging industry continues to evolve as companies seek better performance and sustainability. Several trends shape the use of laminated aluminum foil today:
Manufacturers introduce innovations like SEL Tiger Foil, which focus on food safety and product variety.
Brands such as Capri Sun now use recyclable pouches made from aluminum, PE, and PET, offering a lower carbon footprint than traditional PET bottles.
Mergers and acquisitions, such as Constantia Flexibles acquiring Aluflexpack, help companies improve manufacturing and development capabilities.
Companies like Hindalco have launched 100% recyclable aluminum-foil-laminated jute bags to replace single-use plastics.
The market for packaging laminates grows as demand for longer shelf life in food and pharmaceuticals increases.
There is a strong shift toward sustainable and recyclable materials, including mono-material laminates and solvent-free adhesives.
Regulatory pressures and consumer preferences push brands to reduce material complexity while maintaining barrier performance.
Emerging economies drive growth due to rising incomes and expanding retail infrastructure.
Raw material cost volatility affects manufacturing costs and scalability.
Plastic-based laminates dominate the market because of their versatility, cost efficiency, and barrier properties, with flexible packaging formats like stand-up pouches gaining popularity.
Research and development investments focus on balancing performance with environmental goals, including the use of recycled content and eliminating substances of concern.
Manufacturers also move toward mono-material films to improve recyclability. Some companies replace or supplement aluminum foil with metallized plastics or bio-based plastics to reduce the carbon footprint. However, laminated aluminum foil remains essential for applications that demand the highest barrier properties. The industry continues to balance the need for protection, sustainability, and cost.
Note: As the industry advances, laminated aluminum foil adapts to meet new challenges, making it a reliable choice for modern packaging needs.
Laminated aluminum foil improves packaging by delivering strong barriers, flexibility, and durability. Many industries rely on laminated aluminum foil to protect food, medicine, and sensitive products. The table below shows its growing role in modern packaging:
| Material Type | Market Share / Usage | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Foils | Approx. 18% of flexible packaging market | Pharmaceuticals, dairy, ready-to-eat meals |
| Plastics (PE, PET) | Approx. 49% of flexible packaging market | Food & beverage, healthcare, personal care |
| Pharmaceutical Use | 62% of blister packs are aluminum-based | High-barrier packaging for moisture/oxygen |
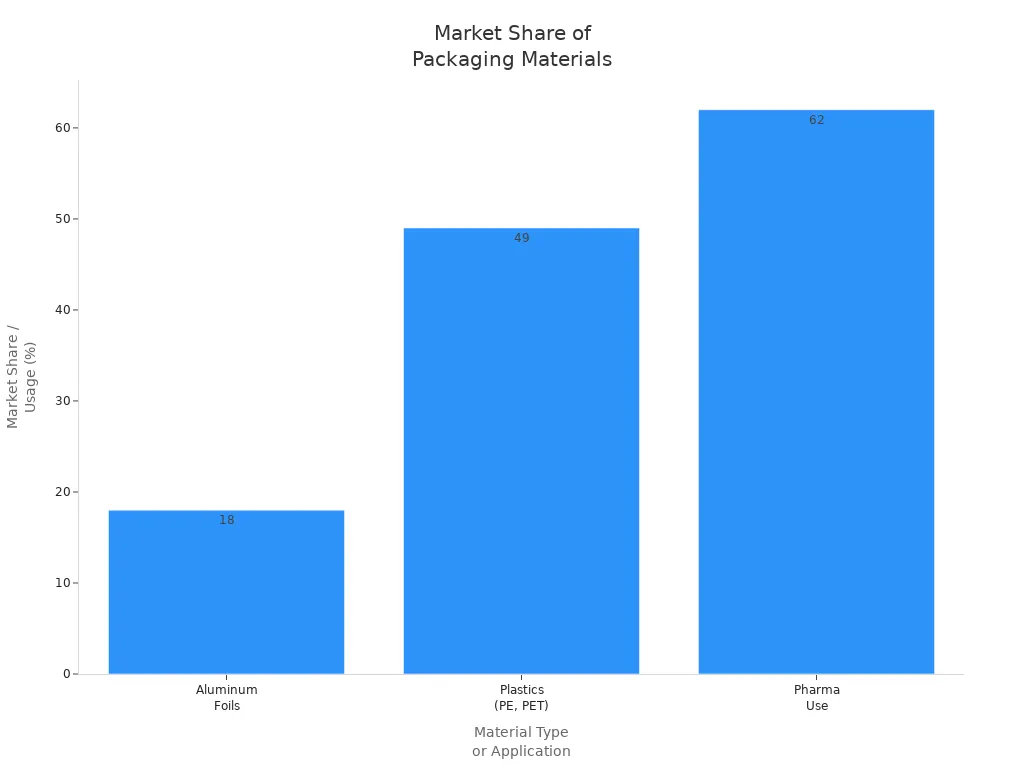
Laminated aluminum foil remains a preferred solution because it extends shelf life and maintains product quality. Companies continue to choose laminated aluminum foil for its unmatched protection and performance. As demand rises, laminated aluminum foil will shape the future of safe, reliable packaging.
Aluminum foil blocks light, oxygen, and moisture. PET adds strength and protects the foil. PE allows for heat sealing. Together, these layers keep products safe from spoilage and contamination.
Yes. Many companies use aluminum foil laminated PET PE film for food and pharmaceutical packaging. The film meets safety standards and protects sensitive products from air, moisture, and light.
Most recycling centers cannot process this film because of its mixed layers. Some new designs use mono-materials for better recycling. Always check local recycling guidelines before disposal.
The film blocks oxygen, moisture, and light. These barriers slow down spoilage and keep products fresh longer. Many foods and medicines last much longer when packaged with this film.
Manufacturers use this film for pouches, bags, sachets, and wraps. It works well for snacks, coffee, pet food, pharmaceuticals, and industrial products. The film adapts to many shapes and sizes.
Yes. Some companies now use recyclable mono-material laminates or films with special coatings. These options offer good barrier protection and help reduce environmental impact.
No. The film acts as a neutral barrier. It does not react with food or medicine. Products keep their original taste and aroma.
Laminated aluminum foil uses a thicker foil layer for maximum protection. Aluminized PET film has a thin metal coating. Laminated foil offers better barriers, while aluminized PET is lighter and more flexible.